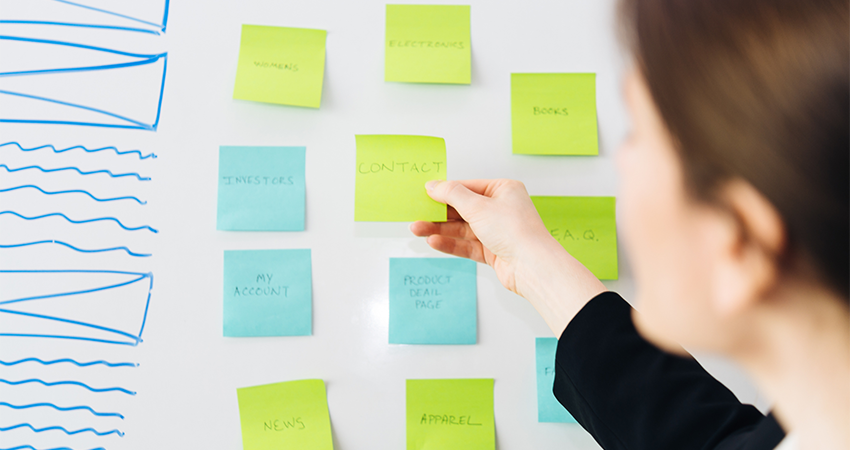
What is Card Sorting in UX and what is it for?

Card Sorting is a UX Research technique that will help you create a comprehensive and intuitive structure and navigation for your application. It involves creating a set of cards that represent the navigation of a site, with the goal of having the user organize them according to what they find most logical.
Does the structure of your site make sense to users ?
If they had to search for a product on your page using only the navigation menu, would they be able to find it easily?
Or if they wanted to return a product, could they quickly find the section where they can do this task?
Or maybe your user simply doesn't understand the structure and navigation of your platform?
If you want to improve the structure of your site, the Card Sorting technique can help you.
What is Card Sorting?
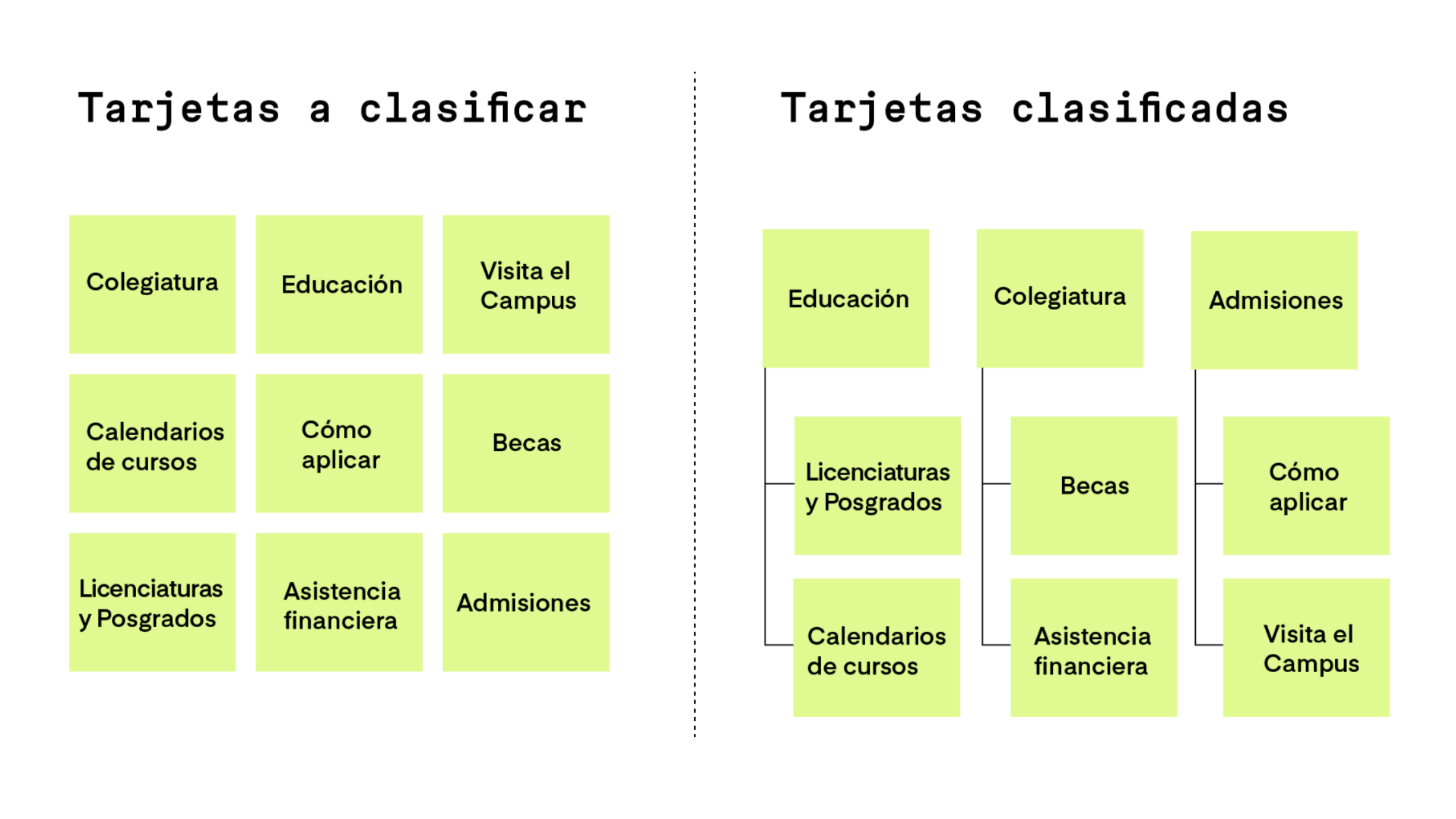
Card Sorting, is a UX Research technique that will help you create a comprehensible and intuitive structure and navigation for your application's user. It consists of creating a set of cards that represent the navigation of a site, with the aim that the user organizes them as they seem most logical.
Card Sorting can help you structure information on your platform such as:
Menu
Navbar
Product taxonomy
Settings section
"My account" section
Or any other section that contains a lot of information.
Advantages of Card Sorting
Card Sorting is a methodology with multiple advantages for your company and business. Easy and inexpensive:
Unlike other user research techniques, all you need for Card Sorting are post-its or paper cards. You do not necessarily need expensive software or tools to carry out the work.
Quick to execute
A Card Sorting test can be performed in less than an hour. Preparations beforehand and analysis afterwards may take longer.
Improves the navigation of your site
By knowing how your users would organize your platform, you can create a more simple, understandable and intuitive navigation. As a consequence, you will improve the experience of your customers. You will make your users want to use your platform again, reduce the bounce rate, increase the pages viewed per session, improve the click-through rate, and of course, grow the conversion of your business.
Functional
At the end of the research, you will know the most coherent way to organize your site.
Disadvantages of Card Sorting
Although Card Sorting has multiple advantages, it is not an infallible technique and has a series of problems and challenges that you should be aware of.
Little context
The tool only presents cards with titles to users. It does not provide much context about what application is being structured, what it looks like in real life, or what product or service it sells.
Most of the context could be given with a brief introduction to the participants, but even so, much information could be omitted. For example: icons, current structure, total products sold, photos or images, etc.
Analysis can take a long time
As mentioned above, conducting a card sorting exercise only takes an hour. However, analyzing all the structures proposed by users to propose a single final navigation could take hours or even days.
Varied results
It could be that all users organize the cards extremely differently. If researchers cannot find similarities between all sets of cards arranged, it would not be possible to create a single structure or navigation, making the experiment a failure.
Shallow
Users classify cards without having the entire context of the platform's design. They could organize the cards as they see fit without having the context of the problem you want to solve and without knowing all the specific needs of your company.
Card Sorting Modalities
Card Sorting can be classified into two types: open and closed.
Open
Under this modality, each participant receives a set of cards with words already written by the research team. Participants are asked to arrange the cards in the way that makes the most sense to them. Then they create labels or names for the group of cards they chose.
This modality is commonly used for new information architectures or for categorizing a set of products on a site.
Closed
Researchers decide in advance how the groups of elements are named. Participants are given a set of cards to place each card within a group.
This modality is used when looking to add new elements to an existing information architecture or to obtain further insights after an open card sorting.
Remote vs Physical Card Sorting
Users can perform the classification remotely or physically.
Remote
Users perform card sorting using computer software without the supervision of a moderator.
This method is generally the easiest for researchers, as the software can analyze the results of all participants and reveal which elements are frequently grouped, what category names users created, and the likelihood of two elements being paired.
Physical
The experiment is carried out in a room with all participants. The moderator can give an introduction about what the research is about and what the objective is. If users have any questions, they can consult the moderator.
The observer has the opportunity to see the expression and behavior of the participants while performing the classification. In addition to asking the person at the same time why they made the decision to arrange the cards that way.
How to conduct Card Sorting?
1. Define the information structure you want to redesign
Card sorting is especially useful for structuring your menu or taxonomy of products.
The taxonomy of products is understood as the categories, subcategories of products, and the items that go inside each of them. You can not only structure your menu or product categories but also structure the entire "My Account" section and the tasks that a user can perform.
In this first step, you must determine which part of your site you want to structure.
2. Decide whether it will be an open or closed test
If you want your users to help you structure a new information architecture, you must conduct an open test. For example, if it is the first time you are going to build the taxonomy of your products.
But if you want your users to organize elements on an already created structure, it is best to conduct a closed test. A case would be when you are going to add new products to your catalog and do not know which category to place them in.
3. Prepare the cards
If your experiment will be in person, you will have to prepare a set of post-its or cards for each of the users. If your experiment will be remote, you would have to choose a tool to conduct card sorting and create your set of cards digitally.
4. Select the appropriate participants
This point is very important. Not everyone can participate in your study. You must create an ideal profile of the user of your application.
Here you must answer "Who is the target of my application?" Before integrating a new participant into your study, you must conduct a survey that allows you to confirm that that person would actually use your product in real life.
Normally, it is recommended to conduct the experiment with 15 people.
5. Conduct the study
Once you have selected 15 participants, it is time to conduct your study.
If your study is in person, a moderator should give a brief introduction of what the study consists of and what the objective is. Users should preferably be at least one meter apart from each other. This is to avoid users being influenced by how their neighbor arranges their cards.
The moderator should allow users to arrange the cards in the sequence that they find most logical. The moderator should not give advice or comments on how the cards could be arranged.
Remember, the point is to know how the user would do it. In any case, the meaning of a word that the user does not know can be explained. The researcher leading the session should listen to the comments and see the expressions of the users, without making any positive or negative comments.
Once the users have organized their cards, the moderator should ask each user why they arranged them that way. The user can also be asked if there were some items that were particularly difficult to arrange, or if there were elements that seemed like they could belong to more than one group, or if there is any card that they do not understand.
You should take photos of each set of cards constructed to analyze them after the session is over. Other researchers should participate in the session and take notes regarding what they hear and see regarding the behavior of the participants.
6. Analyze the results
Once you have completed the study, it is time to analyze the results.
You must find coincidences, similarities, and differences between all the sets of classified cards. Look for common groups, category names, or elements that are frequently combined.
If you find that some elements were frequently omitted, determine if it was because the labels on the cards were not clear or the content seemed unrelated to the rest of the themes.
7. Generate a single proposed structure
After analyzing the sets of classified cards and user comments, you must generate a single information architecture. This architecture should be as close as possible to how users


